Explain Different Types of Locks in Sql Server
Define the cursor lock types. Whether locks are taken when data is read and what type of locks are requested.
Locking In Microsoft Sql Server Part 1 Lock Types About Sql Server
It is sensitive to any changes to the original data source.

. Shared locks are placed on all data read by each statement in the transaction and are held until the transaction completes. The proper solution to this problem is to optimize the queries that they dont scan tables end-to-end. The future update might be the very next statement in the transaction.
Indicate that the transaction will modify some but not all resources in the table or page by placing exclusive locks. Block until the exclusive lock on the row is freed. Schema modification Sch-M and.
It is not sensitive to any changes to the data source. This prevents other transactions from modifying any rows that have been. This K type of locking is called implicit locking There are two types of Locks.
Locks are held on SQL Server resources such as rows read or modified during a transaction to prevent concurrent use of resources by different transactions. - Cursors allow row-by-row processing of the resultsets. For example if an exclusive X lock is held on a row within a table by a transaction no other transaction can modify that row until the lock is released.
Shared S Exclusive X Intent shared IS Intent exclusive IX Shared with intent exclusive SIX Shared and exclusive locks correspond to the row-level or page-level locks with the same names. There are 3 kinds of locks in SQL Server i Shared locks - they are used for operations which do not allow any change or update of data. Intent locks sub types.
How long the read locks are held. There are 2 different types of deadlocks. Update locks are used when SQL Server intends to modify a row or page and later promotes the update page lock to an exclusive lock before actually.
Other sessions can still see the data. Schema locks Sch The SQL Server database engine recognizes two types of the schema locks. A FORWARD_ONLY STATIC Cursor is populated at the time of creation and cached the data to the cursor lifetime.
Indicate that the transaction will read some but not all the resources in the table or page by placing shared locks. Data while executing SQL statements like SelectinsertUPDATEDELETE. The locks acquired to protect data modifications are not affected by the transaction level which is chosen.
Multiple shared locks can be simultaneously set on a resource. OPTIMISTIC - Each time you fetch a row from the cursor it results in a network roundtrip. - It is a database object which is used to retrieve data from a resultset one row at a time.
During Shared locks used concurrent transactions can read a resource but cannot modify the data. Following are the three lock types of cursor. Next time we will look at transaction isolation levels and see how it affects lock behavior.
In other words enable read-committed snapshot on the database. So what we need to remember are basically 3 things. The first is SIU share with intent update which sees a thread with a set of shared locks as well as update locks creating the conflict.
At the table level there are five different types of locks. UPDLOCK is used when you want to lock a row or rows during a select statement for a future update statement. Transaction isolation level in SQL server decides or determines that how transaction integrity is apparent to other systems and users.
Schema modification lock Sch-M and Schema stability lock Sch-S A Schema modification lock Sch-M will be acquired when a DDL statement is executed and it will prevent access to the locked object data as the structure of the object is being changed. The types of schema locks are. Only after that is achieved you can turn your focus to eliminate whatever contention is left.
Retrieve the committed version of the row that existed at the time the statement or transaction started. Shared with intent exclusive SIX Shared with intent update SIU and Update with intent exclusive UIX. The second is SIX share with intent exclusive which takes place when shared and exclusive locks are possessed by a single thread.
At the table level there are five different types of locks. The intent lock shows the future intention of SQL Servers. Lock hierarchy starts from.
Ii Update locks - they are used when SQL Server wants to modify a page. Whether read operations referencing rows modified by another transaction. Shared locks are used for operations that read data such as a SELECT statement.
Shared S Exclusive X Intent shared IS Intent exclusive IX Shared with intent exclusive SIX Shared and exclusive locks correspond to the row-level or page-level locks with the same names. They just cannot obtain locks that are incompatiable with the UPDLOCK andor HOLDLOCK. When SQL Server has the shared S lock or exclusive X lock on a row then the intent lock is on the table.
7 rows Lock Type. Intent shared IS Intent exclusive IX Shared with intent exclusive SIX. Intent exclusive IX Intent shared IS and Intent update IU.
Deploy snapshot isolation based row-level versionning. The update page lock is then promoted to an exclusive page lock before actually making the changes. There are three more types of Forward Only CursorsForward_Only KEYSET FORWARD_ONLY STATIC and FAST_FORWARD.
Cycle locks deadlock definition A cycle deadlock is what happens when a process A which is holding a lock on resource X is waiting to obtain an exclusive lock on resource Y while at the same time process B is holding a lock on resource Y and is waiting to obtain an exclusive lock on resource X. An exclusive lock is assigned for the transaction of any data which holds or modifies the lock data without. X locks are incompatible with any other lock types.
Bulk Update BU Bulk Update used when bulk-copying data into a table and the TABLOCK hint is specified. U locks are compatible with S but incompatible with U Simple enough. S locks are compatible with S and U locks.
Generally use when user want to insert huge data in database Examples of Locks in SQL Server. Shared locks are placed on resources whenever a read operation select is performed.

What Are Sql Server Deadlocks And How To Monitor Them
Types Of Locking In Sql Server Advanced Sql Server Rdbms
Types Of Locking In Sql Server Advanced Sql Server Rdbms
Sql Server Lock Types Chapter 38 Locking And Performance Part V Sql Server Internals And Performance Tuning Microsoft Sql Server 2000 Sql Etutorials Org
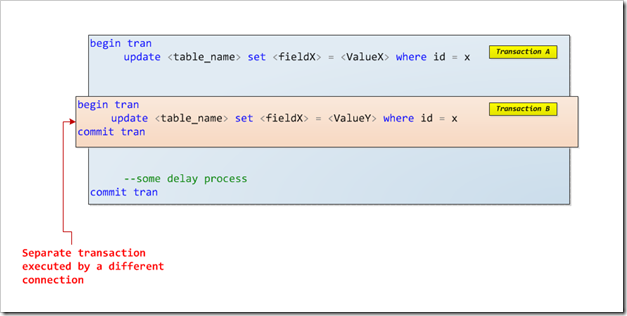
Locks And Duration Of Transactions In Ms Sql Server Codeproject

3 Sql Server Lock Modes Download Table

Sql Server Various Lock Mode Microsoft Q A
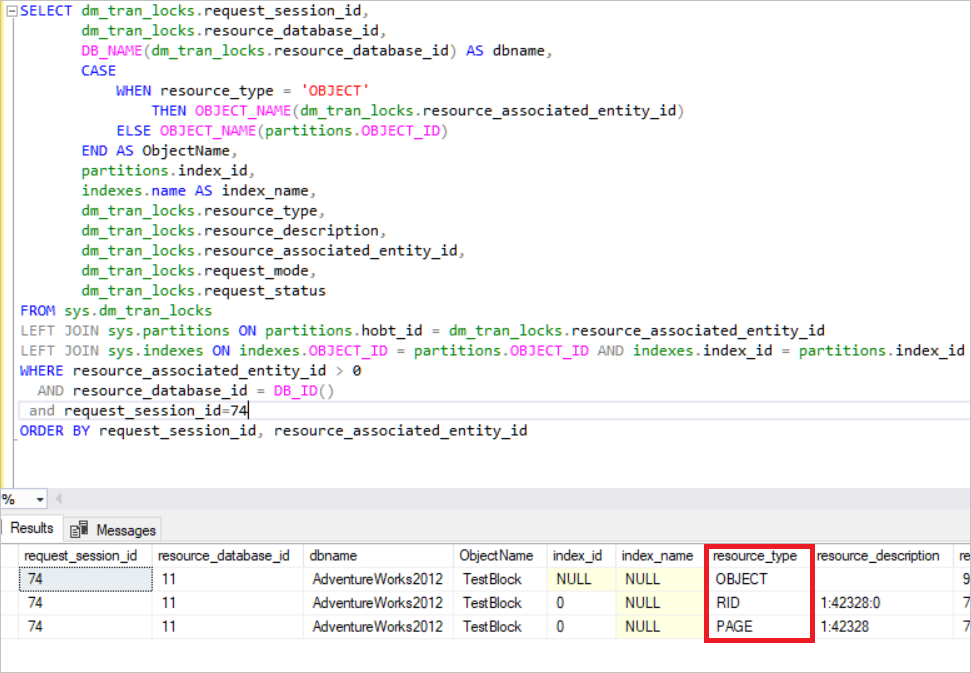
Main Concept Of Sql Server Locking Coding Sight
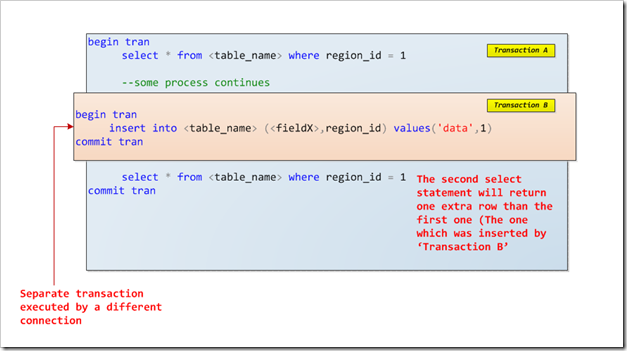
Locks And Duration Of Transactions In Ms Sql Server Codeproject
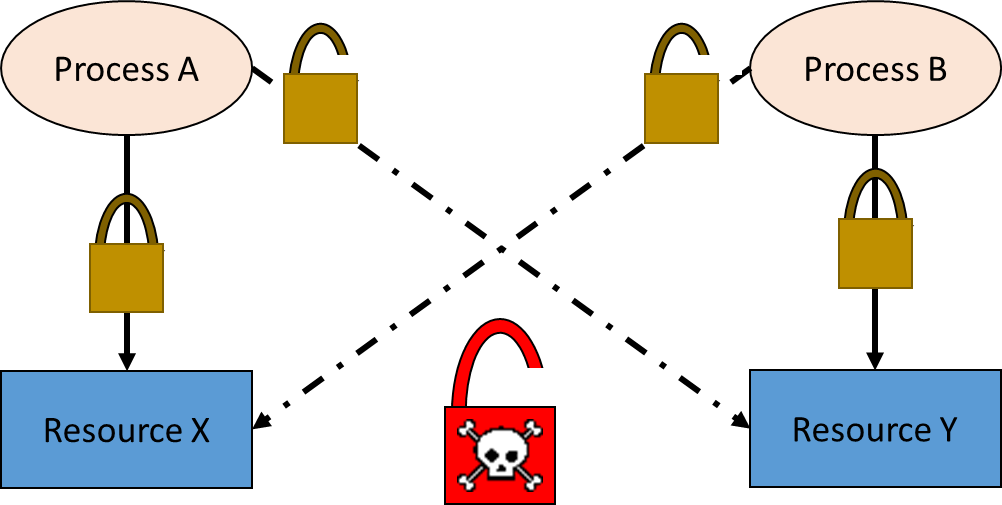
Sql Server Deadlock Definition And Overview
Types Of Locking In Sql Server Advanced Sql Server Rdbms
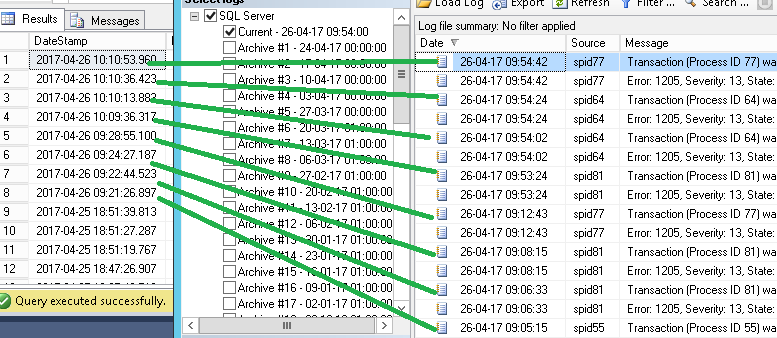
What Are Sql Server Deadlocks And How To Monitor Them
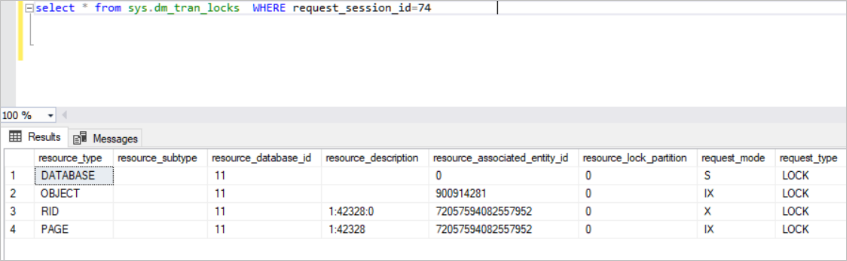
Main Concept Of Sql Server Locking Coding Sight
Types Of Locking In Sql Server Advanced Sql Server Rdbms
Locking In Microsoft Sql Server Part 12 Lock Escalation About Sql Server
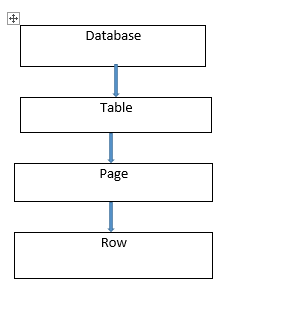
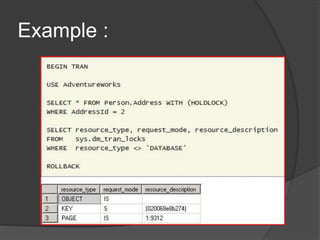

Comments
Post a Comment